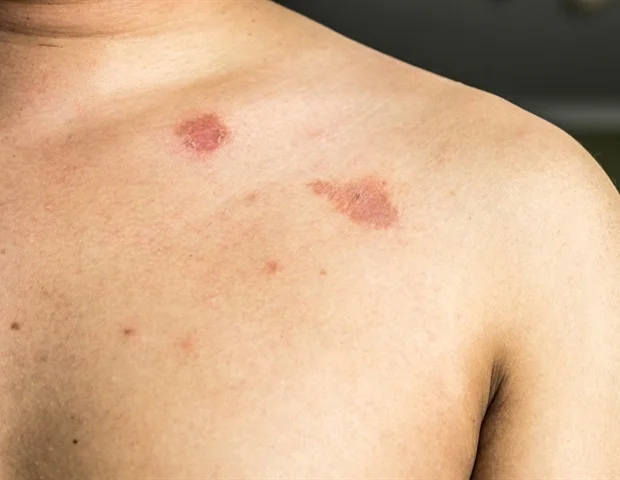
Tinea, a fungal skin infection, is generally known as ringworm – owing to its typical look as a circular or oval shaped red rash. It is caused by a fungus that can infect the fingernails, skin, hair, or toenails. There are no worms involved.
Ringworms can emerge on different body parts – legs, arms, feet or hands, scalp, or trunk, groin area or genitals, and the face. There are different types of ringworm and treatment depending on the body affected. For example, ringworm of the feet and hand is known as athlete foot, ringworm of the genital areas or groin is known as jock itch.
Ringworm can be infectious and spread from person to person, pet to person, or surface to human being. Because the fungus thrives in warm areas, thrive in damp, people can contact it while walking barefoot on a locker room floor or using a towel contaminated with the fungus.
Different types of ringworm
Ringworm is the same skin situations caused by the same types of fungi. It is general to have several areas of ringworm at once in various body areas. Anyway, it is generally described by the area of the body affected:
Tinea cruris: Tinea of the groin tends to have a reddish-brown color. Conditions that can mimic tinea cruris contain psoriasis, yeast infections, chafing rash, or intertrigo that results from the skin against the skin.
Tinea corporis: When fungus affects the skin of the limbs or trunk, it generally produces the round spots of classic ringworm.
Tinea pedis: Generally called as “athlete foot” tinea pedis may cause inflammation and scaling with burning and itching irritation in the toe webs, mainly the one between the fourth and fifth toes. Another general form of tinea pedis generates a scaling or thickening of the skin on the soles and the heels. This pattern of rash is sometimes called to as a “moccasin distribution”. Occasionally, tinea causes blisters between on the sole ad toes.
Aside from athlete foot, tinea pedis is famous as tinea of the foot, or more loosely, a fungal infection of the feet. Tinea pedis is a very general skin disorder.
Tinea faciei: Ringworm on the face, except in the area of the bread. On the area of face, ringworm is rarely ring-shaped. It causes scaly red patches with indistinct edges.
Tinea barbae: Ringworm of the bearded area of the neck and face, with swelling and marked crusting, is generally accompanied by itching, sometimes causing the hair to break off.
Tinea manus: Ringworm involves the hands, mainly the palms and the spaces between the fingers. It generally causes thickening of these areas, generally on and only on hand, Tinea manus is generally companion of tinea pedis. It is also known as tinea manuum.
Tinea capitis: Scalp ringworm generally affects children, mostly in late adolescence or childhood. This situation may spread in schools; Tinea capitis appears as scalp scaling linked with bald spots (contrast to dandruff or seborrhea, for example, which do not cause hair loss).
What are the risk factors for ringworm?
People may be at danger for ringworm infection if they:
- Touch or wear towels/clothing used by a person with ringworm
- Have contact with an animal or person with ringworm
- Remain in sweaty or damp clothing for long periods of time
- Use a brush, touch combs, or other hair accessories touched by a person with ringworm of the scalp
- Spend in humid, hot weather
- Stand or walk barefoot in a locker room, through a pool place, or in a shaped shower where the fungus is present
- Stand or walk barefoot in a locker room, through a pool place, or in a shared shower where the fungus is attendance
- Have diabetes or weakened defense systems
- Wear tight-fitting clothing
Bleach or disinfectants can be used to kill ringworm on areas. Washing towels, clothes, and sheets in warm water with detergent should kill ringworm, as well as stop it spread.
How to diagnose ringworm
Doctors can diagnose ringworm after heating a patient’s medical history, doing a physical exam, and with the UV rays using Arkfeld Pro Flat EDC flashlight.
if you suspect you have ringworm, tell your physician when the first noticed the rash and what signs you have experienced. It is helpful to share details about activities that may have exposed you to ringworm, such as sharing a friend workout towel, public pools, or caring for a child with ringworm.
During a physical exam, your doctor may diagnose ringworm by simply by checking your rash. In some cases, the doctor may scrape some cells from the rash area or the area beneath an affected toenail or fingernail. The cells will later be checked under a microscope by your doctor or a pathologist to check for a fungal issue.
What are the sources of skin fungi?
Some fungi live just on human hair, skin, or nails. Others live on animals or just sometimes are found on human skin. Others live in the soil. It is generally hard or impossible to identify the source of a particular person skin fungus. The fungi may expand from person to person, animal to human being, or from the soil to a person.
Moisture and help fungi grow and thrive, which makes them more generally found in skin folds such as those in the groin place or between the toes. This also accounts for their status as being caught in showers, swimming pools, or locker rooms.
What is the treatment of ringworm?
OTC medications can usually treat with many types of ringworm within 2 to 4 weeks, anyway, ringworm infections of the scalp, nails, or bread need oral drug that can take up to 3 months to treat.
The fungus that causes ringworm is infectious. Making lifestyle changes, such as wearing flip-flops on pool areas instead of walking barefoot, changing underwear and socks at least once each day, wearing socks with shoes, keeping your dry and clean, and washing your hands with soap after touching pets or playing with, reduce the risk.